Recommendations For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease, autoimmune in nature. It is a condition that is often more common in females. In general, it appears in older adults, but it can start at any stage of life. Do you know the recommendations for rheumatoid arthritis?
It is important to consider that, without proper treatment, the disease can cause significant physical limitations in its advanced stages. In addition, over time, it leads to a marked deterioration in the quality of life.
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
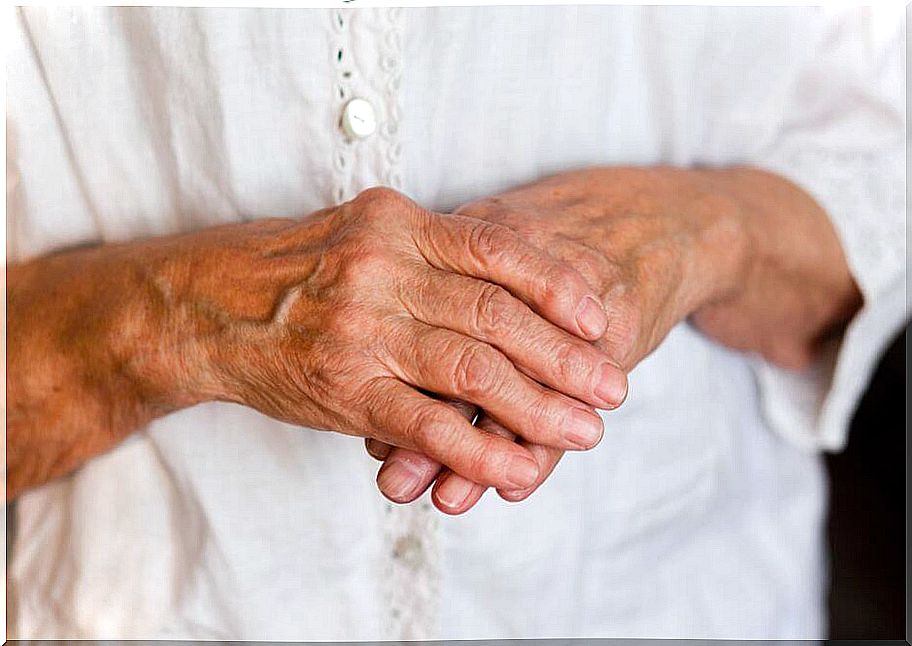

This disease produces symptoms such as pain, swelling, stiffness, or difficulty moving in various small and large joints. General symptoms, which sometimes precede joint manifestations, basically include:
- Tiredness
- Feeling unwell
- Light fever
- Lack of appetite
- Loss of body weight
The possible extra-articular manifestations, which usually occur when rheumatoid arthritis is already established, mainly affect the skin, eyes, heart, lungs and blood vessels.
The most common initial symptom is joint stiffness in the morning, especially in the joints of the hands and feet. It appears after the night’s rest and entails a notable difficulty of movement.
Morning stiffness can be accompanied by tiredness, fever, loss of appetite, and muscle weakness. This set of symptoms sometimes appears weeks or months before pain and signs that denote joint inflammation.
Treatment
Without proper treatment, flare-ups tend to be more frequent and long-lasting. This causes the affected joints to progressively lose mobility and bone deformations occur.
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis consists of a set of measures related to lifestyle, rest and exercise, along with drug therapy.
This set of measures relieves symptoms, improving the quality of life of those affected. The best results are achieved when an early diagnosis is achieved and treatment is established in the initial stages of the disease.
What are the causes of rheumatoid arthritis?
Its causes are not yet fully known. What is known is that it is an autoimmune disorder and that its origin involves genetic causes or factors, as well as non-genetic causes or factors.
Genetic factors
Genetic factors increase the risk of developing the disease. According to the studies carried out on this disease, several genes are involved in its origin.
However, genetic factors only predispose to suffering from the disease, but are not decisive. Although if there is a history of rheumatoid arthritis in close relatives, this constitutes a risk factor to consider.
Non-genetic factors
As for non-genetic factors, there are several to take into account, the following being the most relevant:
- Infections.
- Stress.
- The female hormones.
- Smoking.
- Obesity and the type of diet.
Recommendations for rheumatoid arthritis
Here are a series of recommendations for arthritis, both to relieve symptoms and help it progress more slowly.
- Sleep an average of 8-10 hours. It is recommended that the mattress be hard and the pillow low.
- Reduce episodes of stress.
- Avoid activities that require physical effort, force you to stand for a long time or require repetitive movements, especially with your hands.
- In housework , try not to strain with your hands. There are utensils that can be of great help for housework.
- In periods of low inflammation, it is highly recommended that you do some physical exercise regularly and without getting tired.
- Start the day with a hot bath, which can help reduce morning stiffness or stiffness.
- Practice appropriate exercises to maintain good muscles around the joints. So it is convenient to do exercises without moving the joint, especially if it is inflamed.
- Use devices that maintain the proper position of the fingers of the hands, splints, for night use. This can help prevent future deformities.
- Wear suitable footwear ; elastic but firm, with the attached heel, the wide toe and the high instep.
- Avoid being overweight and obese by following a healthy diet.
Conclution
The evolution of rheumatoid arthritis is highly variable, since in some people it stops spontaneously, while in others it progresses over time.
However, the most common is that it evolves throughout life, alternating periods of flare-ups and periods of relative or absolute calm.









