How Is The Removal Of A Rectal Foreign Body?
Any object introduced into the rectum is called a rectal foreign body. The severity of this situation varies from pain only when defecating to sepsis with multi-organ failure.
Rectal foreign bodies normally lodge in the transition from the anus to the rectum, in an area where the mucosa changes histologically and is narrowed due to the presence of several muscles that contract in a spasmodic manner.
The most common is that they are food remains that were swallowed, but have not been digested. Within this group we find chicken bones, fish bones, seeds, etc. However, they can also be forgotten objects after surgery or erotic toys. Let’s go deeper into this.
How is the clinic of a rectal foreign body?

An article in the Merck Manual points out that the most common sign is pain in the anal region. It is an intense pain that is not related to defecation, although it is possible that it worsens during this process due to the increase in pressure.
In some cases, perforation of the rectal mucosa may occur; if so, the patient would have continuous glittering bleeding. This clinical sign is called “rectal bleeding” and is a risk factor for contracting an infection by the bacteria that make up the rectal microbiota or flora. In addition, it can be accompanied by tears that would cause anal fistulas or fissures.
The worst-prognosis complication is irritation of the peritoneum. These cases are usually accompanied by sepsis; that is, we would speak of a disseminated infection that can trigger a multiorgan response with shock in the patient.
A complete medical history is usually sufficient to describe the lodged object. In addition, it is important to ask the patient if they have noticed abdominal discomfort or difficulty in defecating. The stopping of intestinal transit produces proliferation of the bacteria present in the fecal matter. In these cases, the patient has a fever and signs of inflammation.
How are rectal foreign bodies located?
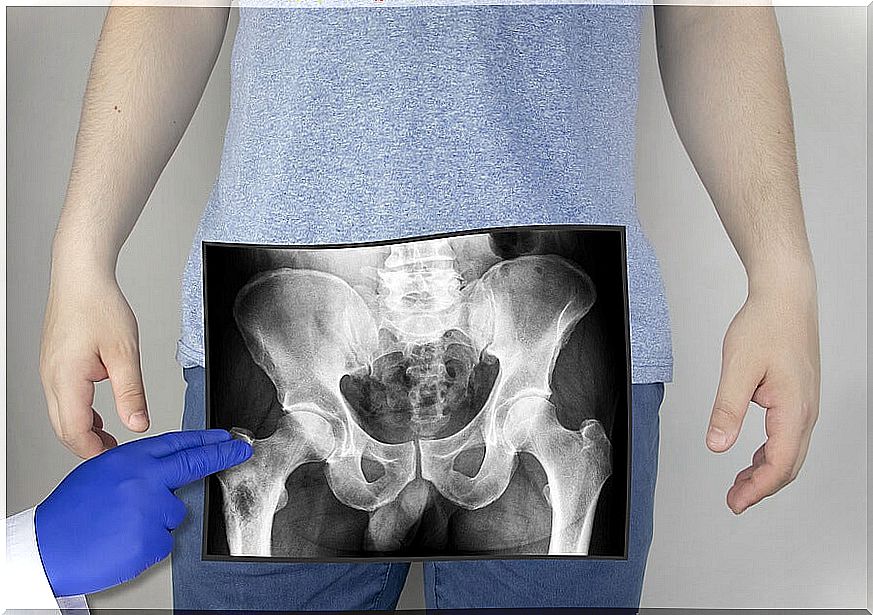
The first thing to do to locate the object is an exploration using imaging techniques. In these patients, a digital rectal examination is contraindicated since it would help to introduce more of the foreign body.
The most common is to take an X-ray since most foreign bodies are visible through the use of X-rays. The best projection to visualize the object is a posterior plane where the entire pelvis is seen.
An imaging technique must always be performed to rule out perforation of the rectum. Once this complication is ruled out, it is planned which action is the most advisable according to the characteristics of the object (size, shape and location).
In the event that the object is palpable, it is extracted directly using anal dilators. The area is anesthetized by applying anesthetic ointments or injection of local anesthetic, and then a rectal retractor is inserted that allows access to the foreign body.
If the X-ray reveals that the object is in a deep plane, surgery is necessary. These surgical interventions are high risk given the area involved. It is a region full of bacteria and, in addition, it is a highly innervated area. Any injury to a nerve can cause incontinence that negatively affects the quality of life of the patient.
Taking these complications into account, it is decided to accelerate the patient’s peristalsis to favor the dragging of the foreign body. In the event of failure, a sigmoidoscope can be used.
As a last resort, surgery would be done using laparoscopic techniques (less invasive, reduce the risk of complications) or colotomy, when no other option is possible.
What steps to take after extraction?

After extraction, a sigmoidoscopy is necessary to assess the status of the rectal mucosa after extraction and to rule out the risk of perforations. In addition, it serves to rule out that the object has been fragmented and that there are remains of it.
Once the results of the imaging test rule out the presence of a foreign body and a rectal perforation, it is necessary to exercise extreme hygiene until the mucosa is completely regenerated.