Why Does Smoking Cause Lung Cancer?
Many people search for the answer to why smoking causes lung cancer. Tobacco is one of the causative agents of various cancers, as it contains thousands of chemical substances and up to 70 of them are carcinogenic, according to experts from the World Health Organization.
Currently there are many evidences that confirm the consumption of tobacco with the appearance of various cancers. Specifically, speaking of lung cancer, it is estimated that almost 90% of this type of cancer is due to smoking.
This causal association was already determined around the 50s, however, today there are still many data that are unknown. For example, it has not yet been determined exactly what the attributable fraction is and there is still no unanimity in the figures obtained by the various population studies.
Despite this, the effects on the body caused by the different substances present in tobacco are currently known. As well as the cellular processes that can be altered and that can culminate in the appearance of cancer.
Chemical substances present in tobacco

Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid, present in tobacco and responsible for addiction to it. The effects of nicotine in the body occur at the level of the central nervous system (CNS), by interacting with the nicotinic receptors in the brain.
When nicotine binds to these nicotinic receptors in neurons, they release chemicals called neurotransmitters. Some of these released neurotransmitters are acetylcholine, dopamine or norepinephrine.
The physiological effect caused by the release of these substances in the brain generates a feeling of calm and pleasure. Since nicotine has a half-life of 2 hours in the body, decreases in nicotine levels and consequent decreases in these substances, will produce withdrawal symptoms. This is precisely why tobacco causes addiction.
Finally, nicotine is also one of the main and most abundant carcinogenic substances in tobacco that answers why smoking causes lung cancer. However, there are many others with harmful effects on the body.
Other substances
Tobacco smoke contains thousands of chemicals, formed from the combustion of chemicals in cigarettes. Within these compounds, there are, as we have mentioned, at least 70 that are carcinogenic.
Some of these chemicals are as follows:
- Lead.
- Benzene.
- Nitrosamines.
- Carbon monoxide.
In addition to cancer, these substances can also cause conditions such as heart or lung disease.
Lung cancer
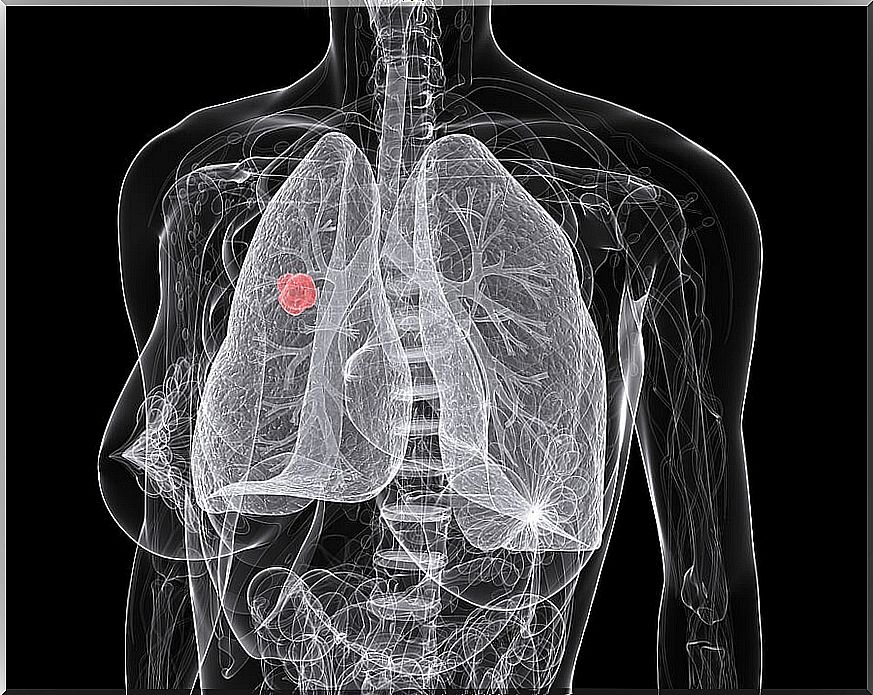
Lung cancer includes different types of lung carcinomas, such as: squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma and large cell carcinoma.
All these subtypes of lung cancer involve the existence of cancer cells that proliferate uncontrollably, generating malignant tumor masses in the airways or alveoli. When these tumor masses grow, they generate respiratory symptoms by affecting normal lung function.
Lung cancer has one of the lowest survival rates, being the leading cause of cancer death. Its high mortality lies in the difficulty to diagnose it early and therefore it is especially important to carry out detection tests, especially in those patients who belong to the risk group due to their history of smoking.
According to experts from the American Cancer Society , risk factors associated with lung cancer are:
- Smoking
- Maintain bad eating habits.
- Having received radiation therapy to the chest.
- Secondhand smoke (being a passive smoker).
- Having a personal or family history of lung cancer.
- Being exposed to radon (a natural gas that comes from rocks and soil) or other substances, such as arsenic, asbestos, diesel emissions, etc.
The role of tobacco in the development of lung cancer
It is logical that the lung is one of the organs most affected by tobacco. Well, it is the main route of contact and deposit of carcinogenic substances. In this way, carcinogens in smoke will accumulate in the respiratory tract and alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
The effects of these carcinogens on cells can vary from one another. Thus, there are substances that have to be metabolized by the cell to become carcinogenic, while there are others that are already carcinogenic.
Today, it is known that these types of substances can cause cellular alterations by having a high mutagenic potential. This implies that cells undergo alterations (mutations) in their DNA.
These mutations often end up affecting certain genes involved in the development of cancer, they are called proto-oncogenes. However, mutations in these protoncogenes can turn them into oncogenes, that is, genes that when expressed will alter the correct cellular functioning favoring the appearance of cancer.
However, tobacco is also involved as a causative agent of other types of cancer, apart from lung cancer. For example: cancer of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, cervix, bladder, kidney, pancreas and prostate, among others.
Is smoking worth it?
In short, carcinogens inhaled with tobacco smoke can reach cells and cause mutations in them. If any of these mutations end up altering the cell cycle, increasing the rate of division in an uncontrolled way, the process could lead to cancer.
In this way, we cannot state outright that smoking causes lung cancer, but we can assure that it is a factor that considerably increases the risk of suffering from it.