Tendinitis: Types And Treatment
Repetitive movements, not resting after exercising or some joint diseases such as arthritis can trigger inflammatory processes in the tendons.
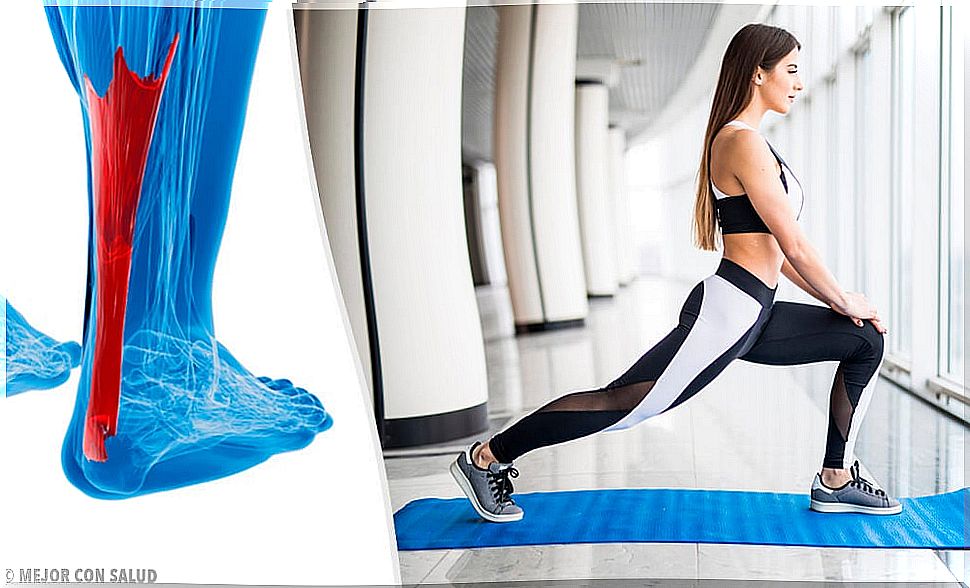

Tendinitis is a pathological inflammation of the tendons, located inside the joints. Although it can affect any tendon, there are certain areas where this disease is more likely to appear.
Tendons are a collection of high-strength fibers that act as a link between skeletal muscles and bones. In this way, the kinetic energy generated in the contraction of the muscle is transmitted to the corresponding group of bones and the movement is executed.
Causes of tendonitis
The most common cause of tendonitis is joint overload. People who overwork a joint can wear down tendons and inflammation of the same occurs as a response mechanism.
Some professions increase the risk of suffering from this disease, either due to the daily load of heavy objects (such as the construction sector) or by practicing sports that require a greater joint effort (tennis, golf, etc.).
As a consequence of joint degeneration, tendonitis can also appear. Usually, this situation is related to aging, which is why it becomes a common pathology in older adults.
However, some diseases that present with a picture of joint inflammation (such as arthritis) are also usually accompanied by tendinitis.
Types of tendonitis
We can differentiate different subtypes of tendonitis, depending on the area where the injury occurs. The most common are the following:
- Shoulder. It is the most common variety. In a high percentage of patients the inflammation is due to aging. However, sportspeople who play baseball or tennis are also prone to this ailment.
- Elbow. It is usually related to tennis, climbing or golf.
- Heel. It occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed. People who practice athletics on a daily basis have a high probability of suffering from it. In addition, it is the subtype of tendinitis that appears most frequently associated with arthritis.
- From doll. It occurs in the flexors of the hands and is associated with climbing and writing a lot on the computer.
Tendonitis signs and symptoms
All tendinitis are characterized by localized pain that is aggravated by movement. Patients experience severe pain along the damaged tendon and in the affected joint area. Normally, this pain intensifies when performing movements that involve that joint and during the night.
For this reason joint stiffness sometimes appears first thing in the morning. In addition, the area of the injury may show swelling, increased temperature, and even local redness due to local inflammation.
Diagnostic methods
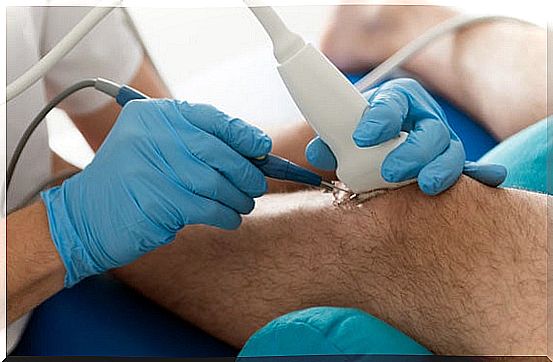
Tendinitis is usually diagnosed with a physical examination that is accompanied by compatible symptoms. Only in those cases when the diagnosis is not clear or there is suspicion of another disease can other diagnostic imaging techniques be used. The most widely used tests are ultrasound and radiography.
Tendonitis treatment
The main objective of the treatment is the elimination of the pain of the joint whenever it is possible, or in its absence, to help to reduce it. To do this, different methods are used:
- Drugs. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are mainly used to reduce inflammation of the tendon. They can be administered systemically or in the form of ointments to apply to the injured area.
- In some cases, glucocorticoids can be used.
- Application of heat (during the first 3 days) to increase blood flow, relax muscles and promote the recovery process.
- Joint immobilization. For this, splints and other orthopedic accessories are used.
- Physiotherapy. A more than recommended measure to guarantee relief to the patient, as it allows a gradual recovery of the tendon, avoiding possible sequelae and recovering joint mobility.
- Transcutaneous nerve stimulation therapy.
- Surgery (only in severe cases).
Tendonitis prevention

To keep our body stable and healthy, it is necessary to exercise regularly. However, we must avoid repetitive movements in our daily lives that overload the tendons and joints. For this reason, we must rest after each series of exercises, allowing the recovery of the area.
If we notice any condition or pain while performing an activity, it is advisable to completely stop the practice and consult a doctor to avoid further aggravating the injury. Under no circumstances is it recommended to ignore discomfort or self-medicate with over-the-counter anti-inflammatories.