Hearing Loss: Symptoms And Treatment
Hearing loss affects 360 million people worldwide. The probabilities of suffering from this pathology increase with age.

Hearing loss is ultimately defined as hearing impairment; that is, inability to hear properly. Thus, listening correctly implies that the organism carries out a series of steps.
First, sound enters the ear canal, collides with the eardrum and causes it to vibrate. This vibration is transferred to a chain of tiny bones that stimulate the cochlea.
Inside the cochlea, there are cells that transform this vibrational information into energy. This energy travels as a nerve impulse through the auditory nerve to the brain stem. From there, the nerve impulse reaches the cerebral cortex. Only then are we aware of the sound.
Depending on the stage of the process that fails, so will the hearing loss. Let’s see, then, its different types, as well as how to treat each one of them.
Types of hearing loss
There are two main types of hearing loss: conductive and sensorineural. It will be conductive when the outer and middle ear (mainly, eardrums and ossicles) are not intact. In the neurosensory type, the cochlea, the acoustic nerve, the brainstem, or the cerebral cortex may be damaged.
Symptoms of hearing loss
Detection of this disease is usually late. This is due to the development of compensatory strategies by the body. There is a wide spectrum of disorders related to hearing loss.
Its main symptom is hearing loss. Low-intensity sounds are generally less distinguishable in conductive hearing loss. However, in the neurosensory, it is difficult to distinguish the sounds, although it is possible to hear their intensity.

It usually happens that high-pitched sounds are heard worse in hearing loss. Because of this, there are fewer problems when it comes to hearing male voices than female voices. In addition, people who suffer from it have difficulty hearing when there are noises in the environment. Even certain sounds can be perceived louder than they really are.
Depending on the cause that generates it, there are some other symptoms that usually accompany deafness. Among the most common are earache or a sensation of atrial fullness if the cause is otitis. If the balance receptor organ in the ear is damaged, vertigo and dizziness may also occur.
Severe hearing loss without effective treatment will lead to communication difficulties. To designate this phenomenon, the term socioacusis was coined. This can have psychological and mood consequences such as depression.
Treatment of hearing loss
To treat hearing loss, it is essential to establish its cause. Thus, depending on the type of hearing loss, one treatment or another will be carried out.
Treatment of conduction hearing loss
When it is caused by a wax plug, it will be removed. If the cause is damage to the ossicle chain, they could be repaired or replaced. If the problem is otitis, antibiotics will be given. In case there is a remnant of fluid from an infection, it will be drained.
In cases of damaged eardrum, either by perforation or by scar as a result of repeated infections, it could be repaired or replaced.
There is also the option of implantable bone conduction hearing aids. These pick up the vibrations that sound produces in the air and transfer them to the inner ear. In this way, the problem of conduction interruption in the outer or middle ear is solved.
Treatment of sensorineural hearing loss
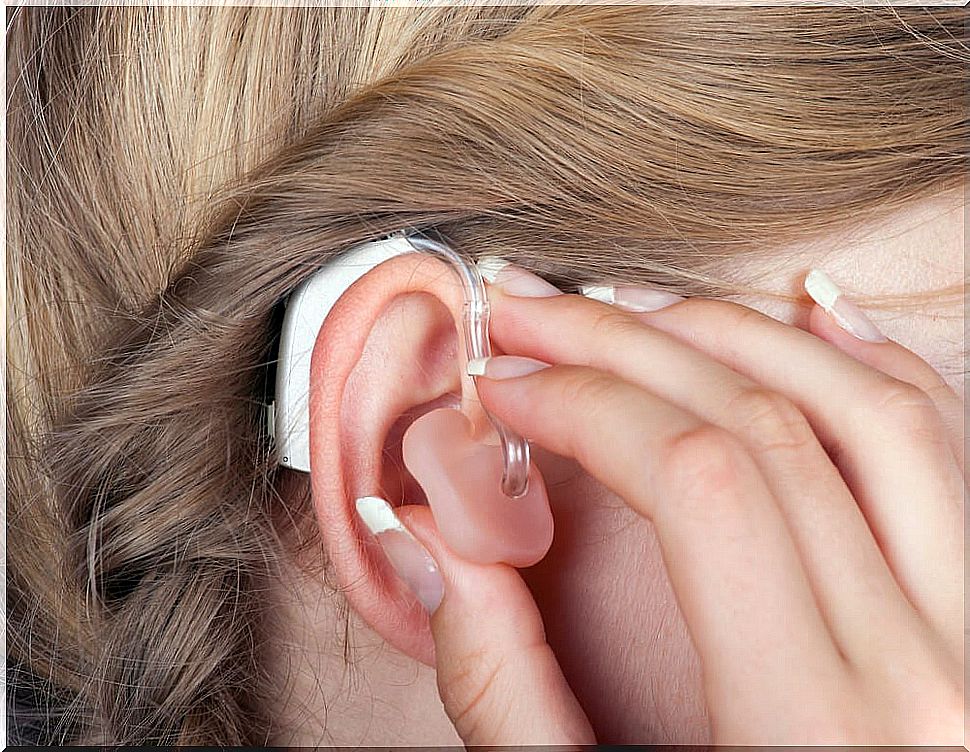
In these cases, the causes are usually not reversible. For this reason, it is usually necessary to implant a prosthesis that performs this sensorineural function. There are implantable and non-implantable prosthetic treatments as therapeutic options.
Non-implantable prosthetic treatments are hearing aids. They modify the sound in one way or another depending on the hearing needs of each patient. Implantable prosthetic treatments are basically of two types:
- Cochlear implants, which replace the function of the organ of Corti.
- Brain stem hearing implants. They directly stimulate this area without the sound having to pass through the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
To conclude, it should be remembered that only a professional with the training for this is the one who must decide the most appropriate therapeutic option.