10 Types Of Fractures You Should Know
Fractures represent the loss of normal continuity of bone or cartilaginous substance. Generally, they are one of the possible consequences of an accident, the results of blows, forces or tractions whose intensities exceed the elasticity of the bone.
Before continuing, it is important to clarify that the term fracture is extensive for all types of bone breaks, from those in which the bone is obviously destroyed and wide, to those very small and even microscopic injuries.
Among the multiple and diverse types , 10 fractures stand out, as they are the most common among those treated by health institutions.
1. Forearm fractures (ulna, radius, or both)
Radius and ulna fractures are caused by a direct impact to the forearm. Its most frequent cause is accidents, be they traffic, sports or a fall from a height. The symptoms that the affected person will present will be:
- Pain.
- Obvious deformity.
- Cries: (abnormal sound heard when listening to the lungs through the chest). These symptoms are accompanied by neurological injury (so you should explore the median, ulnar, and radial nerves).
If an undisplaced fracture is observed on the radiograph, treatment is conservative; if it is displaced, the treatment will be surgical.
2. Humerus fracture
These types of fractures are very common in pediatrics. They are generally due to indirect trauma from a fall on the hand or direct trauma associated with soft tissue injury.
In patients with this type of fracture, the following is observed:
- Pain.
- Deformity.
- Crepitation.
- Loss of joint mobility (the latter linked to the severity of the injury).
Most of these types of injuries require surgical fixation.
3. Hand fractures
Phalanx fractures tend to be more common in children. They are produced by direct trauma to the fingers and indirect rotational trauma. These traumas generate various types of fractures (sometimes due to the entrapment of the hand).
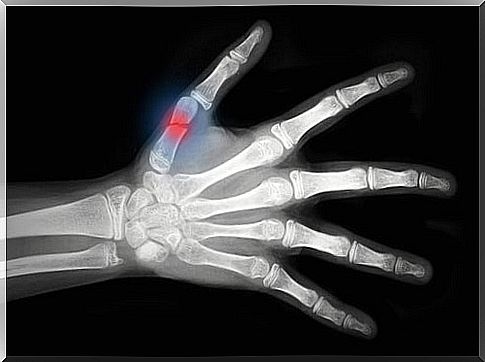
These patients present deformity, pain, and crepitus. Consequently, attention should be paid to vascular-nerve and tendon injuries.
Most phalangeal fractures can be treated conservatively using metal digital splints.
4. Tibia and fibula fractures
Tibia and fibula fractures occur by indirect or direct mechanisms. This mechanism causes transverse fractures (the bone breaks perpendicular in its length) or comminuted (the bone fractures into two or more fragments).
Patients present with pain, deformity, crepitus, and decreased functionality.
- Tibia fractures can be treated conservatively by reduction and stabilization with a cast.
- They can also be treated by surgical stabilization with an endomedullary nail.
5. Clavicle fracture
The most common mechanism that injures the clavicle is a fall with direct trauma to the shoulder (common in cyclists). In these patients, an antalgic attitude is observed (one shoulder is superior to the other) with the injured arm close to the body.
In addition, among the symptoms that they present can be observed: deformity, crepitus and pain in the focus of the fracture.
Treatment consists of shoulder support in a sling or bandage at 8 for 4 weeks.
6. Ankle fractures
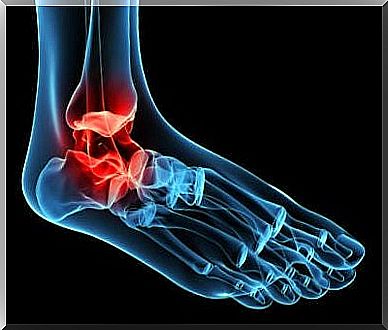
Fractures in this region can be classified into tibial pilon and bimalleolar fractures, that is, when the distal tibia and fibula are injured. These fractures are caused by high- or low-impact mechanisms, usually deceleration forces (such as in a rotational fall of the leg, a sports injury, or a car accident).
The patients present: pain, ecchymosis (bruises), crackles and deformity, as well as decreased mobility. Likewise, depending on the severity of the injury , treatment can be conservative or surgical.
7. Metacarpal fracture
Metacarpal fractures are the result of trauma to the hand, either direct or indirect with torsion. The pattern of the fracture will depend on the mechanism of injury. These patients present with pain, swelling, deformity, and crepitus.
Most cases can be adequately treated with conservative measures.
8. Femur fractures
Hip fracture patients may also have femur fractures. It usually occurs after having suffered a fall or trip, the most frequent being those of the neck of the femur and pertrochanteric. Given its severity, treatment in most cases is surgical.
Patients with this type of fracture have the following symptoms:
- Ecchymosis
- Muscle spasm
- Knee or groin pain
- Inability to walk
- Obvious shortening and external rotation of the affected limb.
9. Radius fractures
Radius head fractures are caused by indirect trauma from landing on the outstretched hand. Patients present with symptoms such as: fork-back or bayonet deformity, crepitus, swelling, and bruising.
In these cases, treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the type of fracture.
10. Nose fractures
Nose fracture is the most common fracture in the facial area. It is a break in the bone or cartilage on the nasal bridge, in the lateral wall or also in the septum (structure that divides the nostrils from the nose).
Patients present the following symptoms: inflammation, bruising and also bleeding. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
To avoid any type of complication and if there is a suspicion of a fracture, one should go immediately to the nearest health center. In this way, it will be possible to corroborate and also solve the present condition.